Weather predictions have become an essential part of our daily life, both in business and leisure. They contribute to safety, efficiency and quality of life to an extent which was hardly imaginable some decades ago. Modern communication means have made weather predictions available to everyone at any minute. Part of the success is the ever-increasing precision and range of the weather forecasts.
Weather predictions for days in advance are always based on synoptic-scale assessments. Measurements of meteorological quantities from all over the globe are fed into numerical forecast models. In a first step, these models assimilate the measured data to create a consistent three-dimensional pattern of the thermodynamic state of the atmosphere at a certain time. In a next step, the laws of physics are applied in discrete time and space intervals with parameterizations of sub-grid processes.
The quality of the forecast depends on the abilities of the forecast model which is connected to the processing power of the forecast computer. It equally depends on the amount and accuracy of the measurement data the forecast is based on. Meteorological research has continuously improved the forecast models, computers have become bigger and faster, and new measurement technologies in large measurement networks provide better input data.
Radar wind profilers more and more become part of the measurement networks used for weather predictions. They provide temporally continuous and vertically resolved wind data in any weather, they also provide temperature when combined with RASS.
With the temporal continuity of their measurements, radar wind profilers stand out. In comparison, radiosondes are only launched a few times per day. Modern assimilation methods can make use of the continuity to improve the quality of the data assimilation and hence of the weather forecasts. Compared to radiosondes, radar wind profilers have two other advantages: They deliver a spatial average over the turbulent fluctuations and they measure at defined locations. In contrast, radiosondes follow the turbulence and drift away while rising. Last but not least, radar wind profilers operate fully autonomous and hence are very economic to use.
Meteorological services worldwide have recognized the potential of radar wind profilers for weather predictions. A more extensive use of radar wind profilers in weather prediction is an established goal and progress is made steadily.
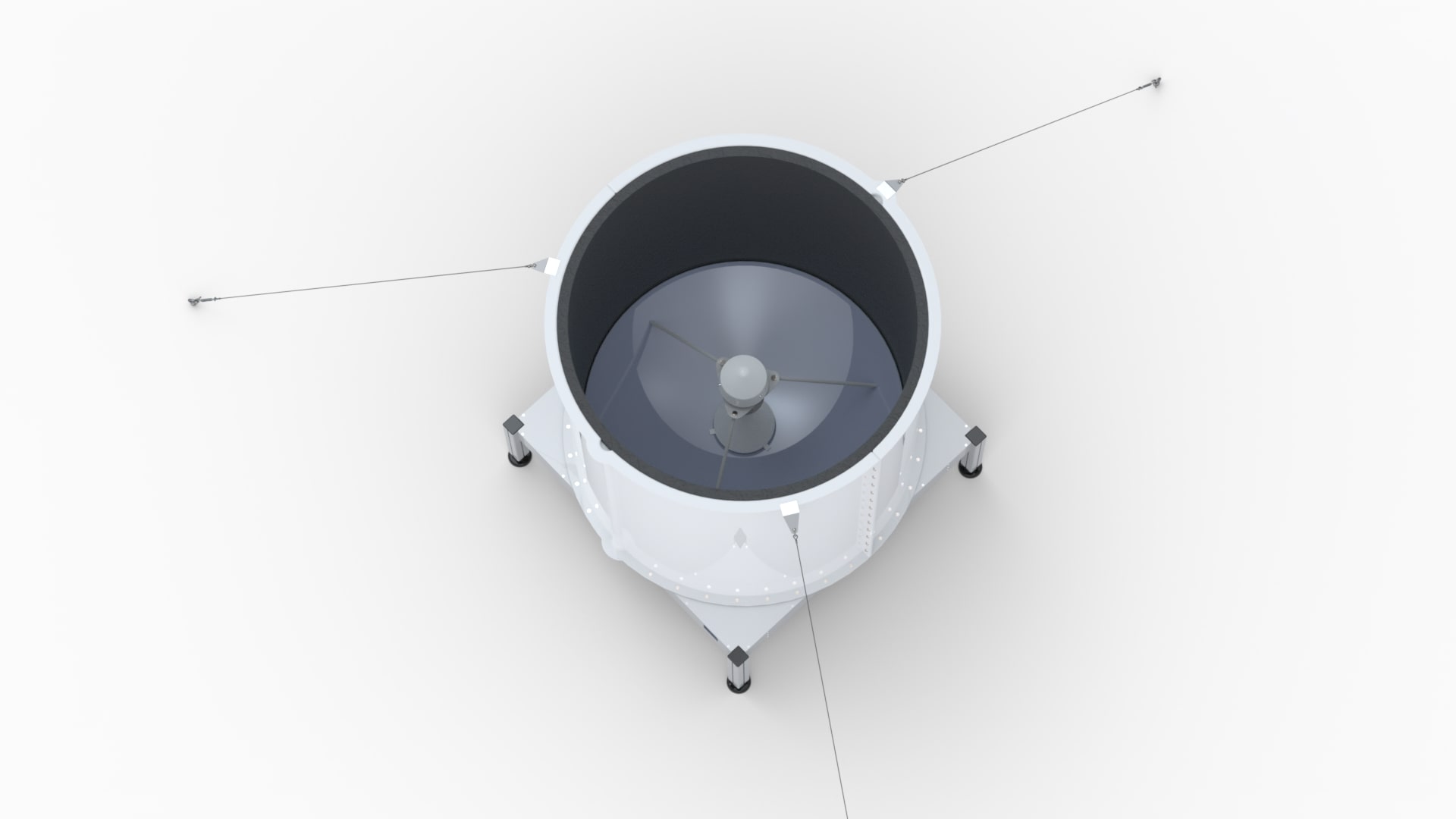

This RASS Extension adds the capability for measuring temperature profiles to a LAP®8000 Radar Wind Profiler.
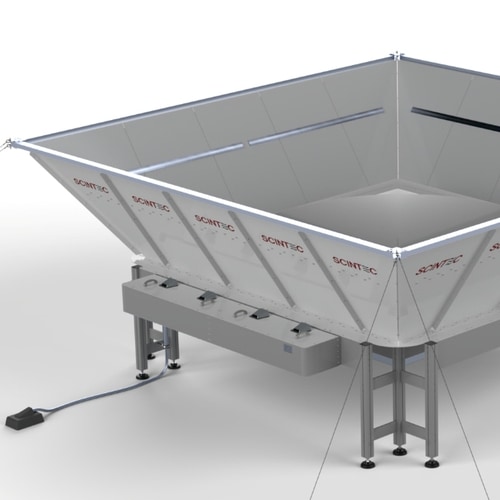

The larger antenna aperture of this model provides the highest performance and clutter resilience that the most critical applications demand.
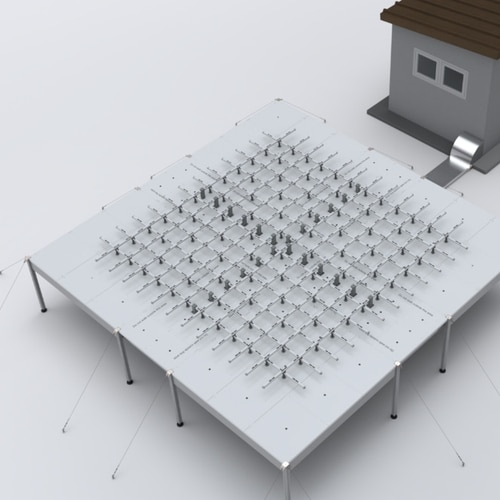
This model operates on a lower radio frequency and achieves the highest measurement range.


